Introduction
The energy landscape is undergoing a profound transformation, with sustainability emerging as a critical driver. At the forefront of this transformation is the quest for cleaner energy sources, and among the contenders, hydrogen has emerged as a versatile and promising candidate. In this exploration of hydrogen's various shades, we delve into the intricacies of its types and their sustainability implications. From grey to blue and green, each hue reflects a unique approach to addressing the energy transition.
This article sheds light on the intricacies of grey, blue, and green hydrogen, unravels the mechanisms behind the generation and utilization of green hydrogen, examines its environmental impact, delves into its applications and advantages, explores the challenges and prospects ahead, and finally, zooms in on India's ambitious green hydrogen journey.
Types of Hydrogen: Unveiling the Colors of Sustainability
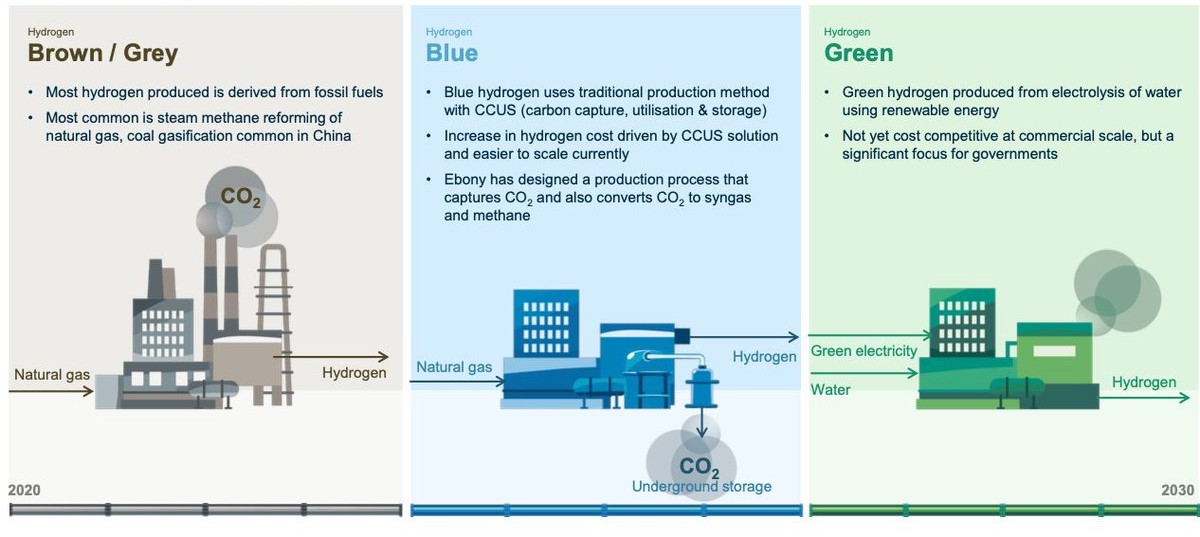
Figure 1: Types of Hydrogen
- Grey Hydrogen: The Dominance of Fossil Fuels Grey hydrogen, primarily derived from fossil fuels like natural gas, prevails as the current dominant hydrogen type. However, its production process emits substantial CO2, contributing to environmental degradation.
- Blue Hydrogen: Progress towards Emission Reduction Blue hydrogen, also sourced from fossil fuels, incorporates carbon capture and storage technologies to mitigate emissions. While a step towards sustainability, it falls short of eliminating emissions entirely.
- Green Hydrogen: Nurtured by Renewable Energies Green hydrogen, also known as renewable hydrogen, stands out as the cleanest and most sustainable hydrogen type. Generated through electrolysis powered by renewable energy sources, it represents a true revolution in decarbonization efforts.
Understanding Green Hydrogen: Origins and Mechanism
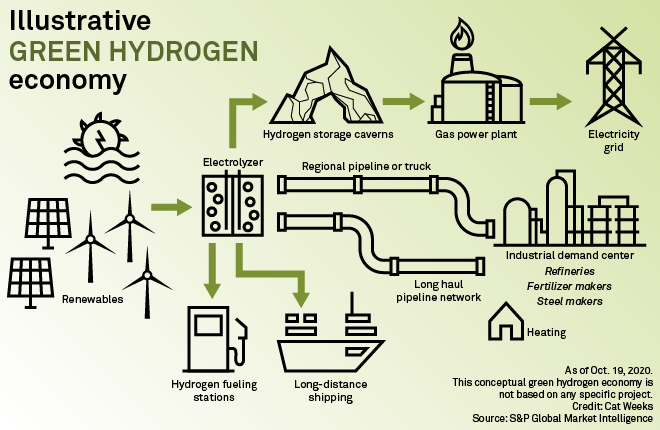
Figure 2: Green Hydrogen Economy (Source: S&P Market Intelligence)
- Generation through Electrolysis Green hydrogen production revolves around electrolysis, a chemical process that utilizes renewable electricity to split water molecules into oxygen and hydrogen. This method ensures zero carbon emissions during the hydrogen generation process.
- The Role of Renewable Energy Renewable energy sources like solar and wind power play a pivotal role in the production of green hydrogen. By harnessing the power of these sources, the process yields hydrogen without contributing to atmospheric CO2 levels.
Environmental Impact
- Reducing Carbon Footprint The production of green hydrogen directly combats carbon emissions. Its process averts the release of around 830 million tonnes of CO2 annually, which is otherwise associated with grey hydrogen production.
- Clean Energy Source Green hydrogen operates as a clean energy source, emitting only water vapor upon utilization. This distinguishes it from conventional fossil fuels, which generate pollutants harmful to the environment.
Applications & Advantages
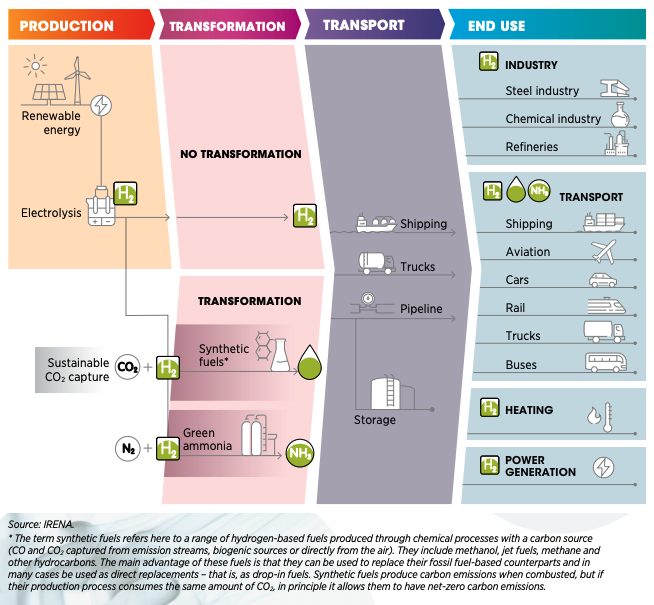
Figure 3: Production, Conversion, and Utilization of Green Hydrogen in the Energy System (Source: IRENA)
- Storing Renewable Energy Green hydrogen offers an efficient method of storing excess renewable energy for extended periods, addressing intermittency issues often encountered with renewable sources.
- Decarbonizing Hard-to-Electrify Sectors The adaptability of green hydrogen makes it a prime candidate for decarbonizing sectors resistant to electrification, such as heavy industry, aviation, and maritime transport.
- Sustainable Electricity Generation Green hydrogen's journey from storage to utilization involves fuel cells, which combine hydrogen with oxygen to generate electricity. The sole by-product is water, aligning with the principles of sustainability.
Challenges & Future Prospects
- Cost and Viability The production cost of green hydrogen remains a challenge, often attributed to the expense of renewable energy sources. However, predictions indicate a decline in production costs as renewable energy becomes more accessible.
- Safety Considerations While highly sustainable, green hydrogen's volatile and flammable nature necessitates stringent safety measures to prevent potential leaks and accidents.
Green Hydrogen: Empowering India's Energy Transition
India has embarked on a visionary path to secure energy independence by 2047 and attain Net Zero status by 2070. In pursuit of these ambitious targets, India recognizes the pivotal role of renewable energy adoption across its economic sectors. Among the arsenal of strategies for this energy transition, green hydrogen emerges as a transformative solution with immense potential.
Green hydrogen takes center stage in India's energy transformation narrative. With its diverse applications, it holds the potential to redefine the energy landscape of the nation. As India aims to increase renewable energy deployment, the integration of green hydrogen becomes a linchpin for achieving its energy objectives.
Multi-Faceted Utility of Green Hydrogen
Renewable Energy Storage: Green hydrogen's capacity for long-duration energy storage perfectly aligns with India's energy demands. It can absorb surplus energy generated during peak renewable production periods and release it when needed, providing stability to the grid.
Industrial Decarbonization: The substitution of fossil fuels in industries with green hydrogen could significantly curtail carbon emissions. This transition paves the way for a sustainable industrial landscape, contributing to India's emission reduction goals.
Clean Transportation: Green hydrogen-powered vehicles present a cleaner and greener alternative to conventional transportation modes. This could alleviate India's pollution woes while promoting sustainable mobility.
Decentralized Power Generation: The prospect of decentralized power generation using green hydrogen holds the potential to electrify remote areas that are often disconnected from the grid.
Aviation and Marine Transport: India's aviation and maritime sectors could experience a paradigm shift through the adoption of green hydrogen, fostering cleaner and more sustainable travel options.
National Green Hydrogen Mission: An Integrated Approach
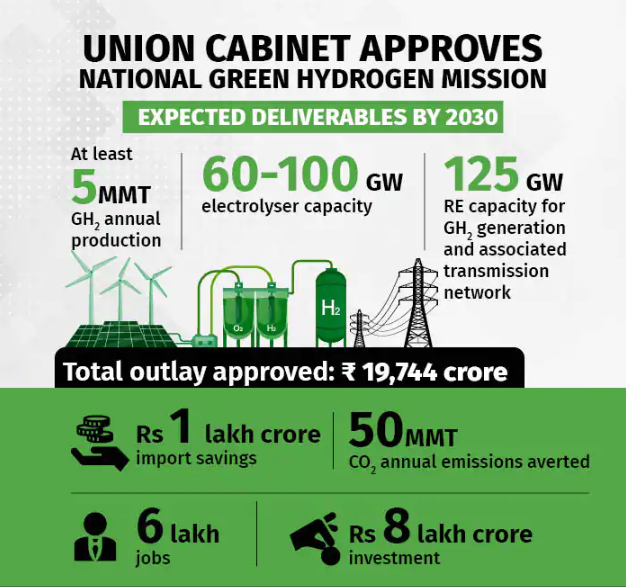
Figure 3: National Green Hydrogen Mission (Source: moneycontrol)
India's National Green Hydrogen Mission, approved on January 4, 2022, exemplifies the nation's commitment to harnessing the potential of green hydrogen. The mission is strategically designed with multiple objectives in mind:
Global Leadership: India aims to emerge as a global leader in green hydrogen production and supply, underscoring its commitment to sustainable energy solutions on a global scale.
Export Opportunities: The mission seeks to create export avenues for green hydrogen and its derivatives, positioning India as a significant player in the international energy market.
Reduced Dependence: By substituting imported fossil fuels with green hydrogen, India aims to reduce its reliance on external energy sources, enhancing energy security.
Domestic Manufacturing: The mission fosters the development of indigenous manufacturing capabilities, driving economic growth and self-reliance.
Investment and Employment: The initiative is poised to attract substantial investment, creating a wealth of business opportunities and generating employment prospects.
Research and Development: With a focus on R&D, the mission spurs innovation and technological advancements in the green hydrogen sector.
Anticipated Outcomes:
By 2030, the National Green Hydrogen Mission aims to achieve remarkable milestones:
Capacity Expansion: A green hydrogen production capacity of at least 5 Million Metric Tonnes per annum will be established, accompanied by an addition of about 125 GW of renewable energy capacity.
Economic Impetus: The mission is projected to attract over Rs. Eight lakh crore in investments and generate employment for over six lakh individuals.
Reduced Imports: Cumulative savings of over Rs. One lakh crore from decreased fossil fuel imports is anticipated.
Environmental Impact: By abating nearly 50 Million Metric Tonnes of annual greenhouse gas emissions, the mission significantly contributes to India's climate goals.
As India marches toward a sustainable and greener future, green hydrogen takes center stage, promising a transformative impact on energy, economy, and environment alike.
Collaborative Efforts: Verra and Gold Standard Join Forces for Hydrogen Methodologies

In a significant development for the hydrogen industry, the two largest carbon standards globally, Verra and Gold Standard, have announced a collaborative endeavor to create a unified set of carbon methodologies. This joint effort aims to accelerate the adoption of hydrogen as a commodity within the broader energy landscape.
- Hydrogen's Role and Challenges: Hydrogen, hailed as a carbon-neutral energy carrier, holds immense potential for the energy transition due to its diverse production methods, including those involving green electricity. Despite its promise, hydrogen remains more expensive than fossil-based energy sources. Although Europe has witnessed the announcement of several hydrogen projects, the global pace of implementation has been relatively slow, particularly outside of Europe.
- The Significance of Carbon Methodologies: Carbon methodologies serve as foundational guidelines for generating carbon credits under voluntary schemes and could potentially be incorporated into the framework of the Paris Agreement in the future. The collaborative effort between Verra and Gold Standard, known as the Hydrogen for Net Zero Initiative (H2NZ), seeks to establish common methodologies that span both standards. The initiative was initially introduced by Consultancy Perspectives in partnership with the South Pole and is now expanding its scope and timeline.
- Timeline and Ambitions: The work on H2NZ is scheduled to commence in September, with the goal of unveiling comprehensive methodologies within 18 months. These methodologies will encompass the entire hydrogen supply chain, covering aspects from production to transportation and storage. Flexibility is key, as the methodologies need to cater to various end-use sectors.
- Encompassing the Full Spectrum: The ambitious aim of H2NZ is to provide methodologies that address a wide spectrum of applications across the hydrogen value chain. This inclusivity is crucial, as the unique requirements of different sectors, such as the chemical industry and the steel sector, necessitate tailored approaches. By embracing this comprehensive approach, the initiative sends a robust signal to the hydrogen community that carbon markets are fully committed to supporting the integration of hydrogen as a serious player in the global energy landscape.
As the H2NZ initiative gains momentum, it holds the potential to accelerate the widespread adoption of hydrogen by establishing standardized methodologies that enhance transparency, credibility, and confidence in the industry's carbon reduction efforts.
Conclusion: Pioneering a Greener Energy Future with Green Hydrogen
As the global community navigates the complex terrain of energy transition, green hydrogen emerges as a beacon of hope and transformation. Its potential to revolutionize industries, power transportation, and reshape economies cannot be overstated.
From technological advancements to policy interventions, the journey of green hydrogen is one of collaboration, innovation, and a shared commitment to a sustainable future. India's bold strides toward energy independence and carbon neutrality underscore the significance of green hydrogen in achieving these audacious goals.
By embracing green hydrogen, nations have the opportunity not only to decarbonize their energy systems but also to reshape the trajectory of the planet's sustainability. As the colors of hydrogen continue to evolve, green hydrogen stands out as a beacon of promise, ushering in a cleaner, greener, and more sustainable world.
![[object Object]](/lib_ubcXiSgTRmkLVyyT/k8w528b9mk1p20to.png?w=400)
