Introduction

In the pursuit of achieving sustainable development goals, a groundbreaking initiative has emerged to revolutionize the way social and environmental projects are certified and financed. Verra, a renowned non-profit organization, introduced the Sustainable Development Verified Impact Standard (SD VISta). This flexible framework empowers project developers to define and consistently report on the valuable outcomes of their initiatives, opening doors to new sources of finance and scaling up high-impact efforts.
With SD VISta, the premier standard for certifying real-world benefits, projects spanning from gender equity and economic development to clean energy and wildlife restoration can now be rigorously evaluated. The aim is to enable large-scale investments in sustainable development by providing developers and investors with reliable data on the social and environmental advantages of their projects.
Gone are the days of subjective reporting and uncertain evaluations. SD VISta ensures that project benefits are not only logged but also independently verified, instilling trust and credibility among all stakeholders involved. Expert third-party auditors rigorously assess projects' alignment with the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), guaranteeing their contribution to the global development agenda.
With the estimated annual investment requirement of $5-7 trillion to meet the SDGs, it is evident that the participation of investors whose objectives align with these goals is crucial. SD VISta brings us one step closer to realizing this vision by facilitating transparent reporting, attracting capital, and fostering impactful investments. In this article, we delve into the significance of SD VISta and its transformative impact on the carbon market.
What is SD VISta?
The Sustainable Development Verified Impact Standard (SD VISta) is a game-changing initiative that sets the bar for certifying the tangible benefits of social and environmental projects. From promoting gender equity to advancing economic development, and from facilitating affordable clean energy to restoring wildlife habitats, SD VISta encompasses a broad range of sustainable development endeavors.
SD VISta aims to tackle the challenges surrounding sustainable development investment by providing developers and investors with robust and trustworthy data on the social and environmental advantages of their projects. By employing world-class systems, the standard not only logs project benefits but also subjects them to rigorous independent verification. This verification process ensures the credibility and value of the reported outcomes, instilling confidence among all stakeholders.
To align with the global Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) established by the United Nations, SD VISta engages expert third-party auditors. These auditors assess projects' contributions to the SDGs, guaranteeing their alignment with the global development agenda. By adhering to SD VISta, project developers can confidently showcase the positive impact of their initiatives, attracting investors and capital that share their commitment to sustainable development.
As the need for capital to achieve the SDGs reaches unprecedented levels, SD VISta emerges as a vital tool to bridge the gap between project developers and investors. Its comprehensive and verifiable approach ensures that investments flow into projects that genuinely deliver sustainable development benefits. In the next section, we will explore the implications of SD VISta in driving transformative change within the carbon market.
How does SD VISta work?
Figure 1 (Source: Verra)
Under the SD VISta Program, projects undergo a meticulous certification process to ensure adherence to the program's standards and requirements.
- Certification Guidelines: The program document outlines the specific rules and criteria that projects must comply with in order to achieve certification under SD VISta.
- Independent Evaluation: Qualified independent third parties conduct thorough assessments of all SD VISta projects to verify their compliance with the program's guidelines and requirements.
- Methodological Support: While projects have the flexibility to employ any approach that fulfills the core requirements of SD VISta, Verra provides guidance on suitable methodologies. Additionally, for projects that generate SD VISta assets, Verra offers approval of methodologies.
- Transparent Registry System: Verra maintains a comprehensive registry system that publicly records data on all SD VISta projects. The registry tracks the generation, retirement, and cancellation of SD VISta assets, as well as Verified Carbon Units carrying the SD VISta label, which signifies that the emission reduction unit was generated during a period verified under SD VISta.
SD VISta operates on a robust framework that prioritizes stakeholder engagement and safeguards the well-being of communities, natural capital, and ecosystem services. Projects applying SD VISta must actively involve stakeholders, ensuring their voices are heard, and their needs and aspirations are considered throughout the project's lifecycle. Additionally, the standard incorporates safeguards to prevent any adverse impacts on people and the environment.
To adhere to SD VISta, projects are required to establish a baseline that serves as a reference point for measuring progress. They must quantify the sustainable development benefits generated by their activities and determine the net sustainable development impact of the project. These quantified results are subjected to rigorous verification by independent third-party assessors, ensuring the credibility and reliability of the reported outcomes.
Pilot projects like the initiative led by Conservation South Africa, aimed at improving communal rangelands and creating rural opportunities for the Mnisi and Amashangaan communities, exemplify the potential of SD VISta. These projects showcase the added value of the standard in capturing and reporting on the comprehensive range of "beyond-carbon" benefits, directly linking them to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
“SD VISta is an important addition to the standards offered by Verra,” says Julianne Baroody, Director of Standards Development. “Many projects that are using the VCS and focus on reducing or removing greenhouse gas emissions have additional benefits. While the Climate, Community & Biodiversity (CCB) Standards — which are also managed by Verra — allow land-based projects to demonstrate their climate, community and biodiversity benefits, SD VISta will allow other initiatives to report on other ‘beyond-carbon’ benefits and link these directly to the SDGs.”
SD VISta's comprehensive approach, stakeholder engagement, robust verification process, and integration of "beyond-carbon" benefits position it as a powerful tool to promote sustainable development and attract investments aligned with the SDGs. By providing a transparent and credible framework, SD VISta catalyzes transformative change and fosters the implementation of projects that deliver tangible and multi-dimensional sustainability impacts.
17 SDGs
In 2015, the United Nations introduced the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), also known as the Global Goals, to serve as a universal call to address poverty, protect the environment, and promote peace and prosperity for all by 2030. Comprised of 17 interconnected goals, the SDGs recognize the interdependence of various areas of action, emphasizing the need to achieve a balance between social, economic, and environmental sustainability.
A key commitment of countries is to prioritize advancements for those who are most marginalized and disadvantaged. The SDGs aim to eradicate poverty, hunger, AIDS, and gender-based discrimination, with a holistic approach that encompasses the diverse contributions of society, including creativity, knowledge, technology, and financial resources. Achieving the SDGs requires a collective effort across all contexts to ensure a sustainable and inclusive future for everyone.

The SDGs are an evolution of the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) that were initiated in 2000 and concluded in 2015. The MDGs made significant strides in reducing extreme poverty, improving access to education, and protecting the environment. Building upon this foundation, the SDGs were born from the 2012 Rio+20 Earth Summit and aimed at establishing an ambitious post-2015 development agenda. The SDGs require substantial financial investment, estimated to exceed $4 trillion annually, and differ from the MDGs by incorporating the private sector as a key contributor to sustainable consumption and production patterns.
While some progress has been achieved, challenges remain in meeting the 2030 deadline. The UN reports improvements in areas such as healthcare, with a higher percentage of skilled assistance during childbirth. However, the pace and momentum of SDG implementation have been deemed insufficient by many participants in sustainable development discussions. Poverty reduction has seen limited gains, and the number of undernourished individuals has risen. Gender equality is another area where significant progress is lacking, as highlighted by the SDG gender index, which indicates that no country is on track to achieve gender equality by 2030.
To assess progress and address shortcomings, a gathering of heads of state and government will convene at the United Nations Headquarters in New York in the fall of 2019. This meeting will provide an opportunity to evaluate advancements in the 17 SDGs, as well as discuss updates to targets scheduled for 2020. Meaningful engagement with the private sector and collective efforts across nations will be essential to accelerate progress and ensure the achievement of these critical global goals.
Global Market Trend
The present global market scenario for SD VISta credits indicates a high demand for these credits. The supply of SD VISta credits is predominantly coming from Asian countries, as highlighted by the issuances data.
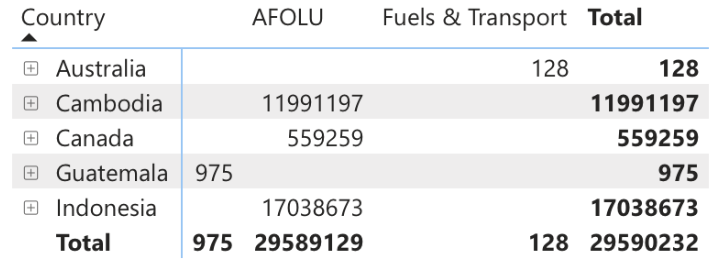
Figure 2: SD VISta Issuances w.r.t countries (Source: Calculus IQ)
Figure 2 demonstrates that Indonesia has the highest amount of issuances, followed closely by Cambodia. Canada ranks third in terms of SD VISta credit issuances, while Guatemala and Australia occupy the fourth and fifth positions, respectively. This distribution of issuances signifies the significant role played by Asian countries as major suppliers of SD VISta credits.
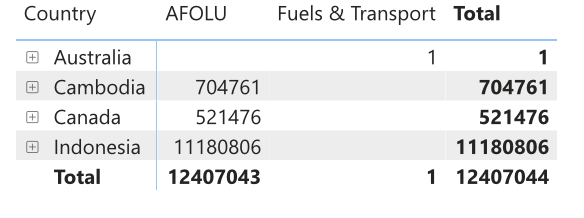
Figure 3: SD VISta credits retired w.r.t countries (Source: Calculus IQ)
As seen in Figure 3, the present demand scenario for SD VISta credits in the global carbon market highlights a strong demand, particularly in Asian countries. Indonesia emerges as the leading country in terms of issuing and retiring the most SD VISta credits. Cambodia closely follows in both issuance and retirement, while Canada secures the third position. These findings indicate that the issuance and retirement of SD VISta credits predominantly occur within the same country.
The high demand for SD VISta credits in Asian countries reflects a growing interest in supporting sustainable development initiatives and addressing Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Organizations and investors in these countries are actively seeking opportunities to contribute to positive social and environmental impacts, aligning their investments with the SDGs.
The fact that SD VISta credits issued in a particular country are often retired within the same country suggests a localized focus on sustainable development efforts. This localized approach may stem from a desire to address specific social and environmental challenges within national boundaries, and also to ensure the accountability and impact of the projects.
As the awareness and adoption of SD VISta credits continue to expand globally, it is expected that the demand will further increase. More countries and organizations are likely to recognize the value of SD VISta credits in supporting sustainable development initiatives, which will drive the demand in the global carbon market.
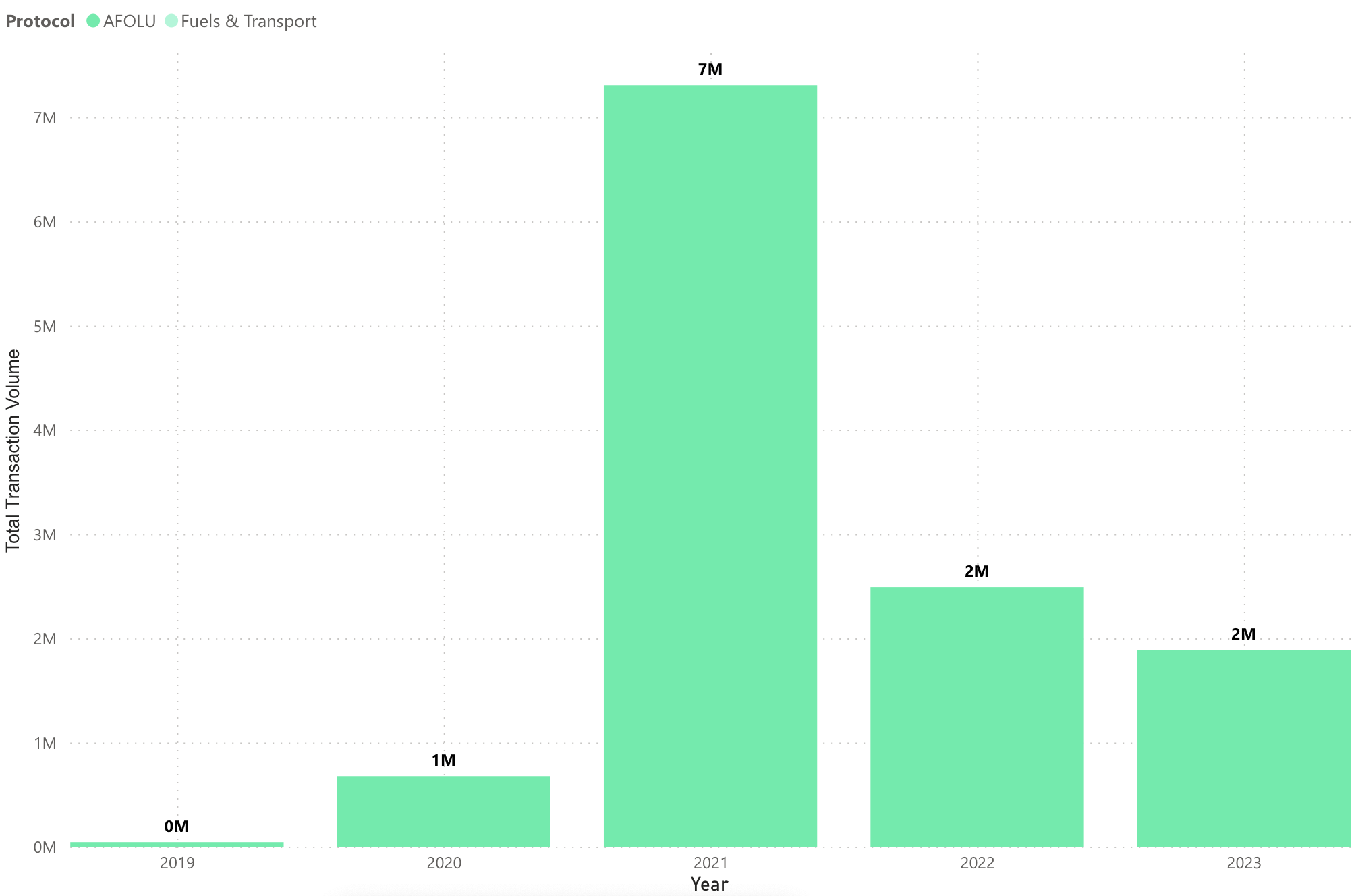
Figure 4: Total Transaction Volume over the years in Metric Tonne (Source: Calculus IQ)
As we can see in Figure 4, From 2019 to 2021, there has been a remarkable increase in SD VISta transaction volumes, rising from 1 million to 7 million metric tonnes in 2021. This surge signifies a growing recognition of the value and impact of SD VISta in supporting sustainable development initiatives worldwide. The substantial growth during this period indicates an increasing demand for these credits as organizations and investors align their investments with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
However, there was a notable decline in transaction volumes in 2022, dropping to 2 million metric tonnes. The decrease could be attributed to various factors, such as market dynamics, regulatory changes, or shifts in investor preferences. Nevertheless, it is essential to note that fluctuations in transaction volumes are not uncommon in the carbon market, and they can be influenced by various factors.
Interestingly, in just one quarter of 2023, there has already been a transaction volume of 2 million metric tonnes, showcasing a potential rebound in the market. This rapid recovery suggests a renewed interest and activity in SD VISta, potentially surpassing the 2021 levels in the coming years.
Based on projections and considering the increasing emphasis on sustainability and the SDGs, it is expected that the transaction volumes of SD VISta credits will continue to experience growth in the future. This upward trajectory can be attributed to the expanding awareness, participation, and integration of sustainable development practices across sectors and regions.
Future Outlook
To gain insights into the future prospects of the SD VISta market, an analysis of the SD VISta pipeline projects database provided by Verra can provide valuable information. By exploring this database, we can identify the regions, countries, and project types that are at the forefront of SD VISta development. This deep dive will offer a comprehensive understanding of the potential growth areas for SD VISta initiatives.
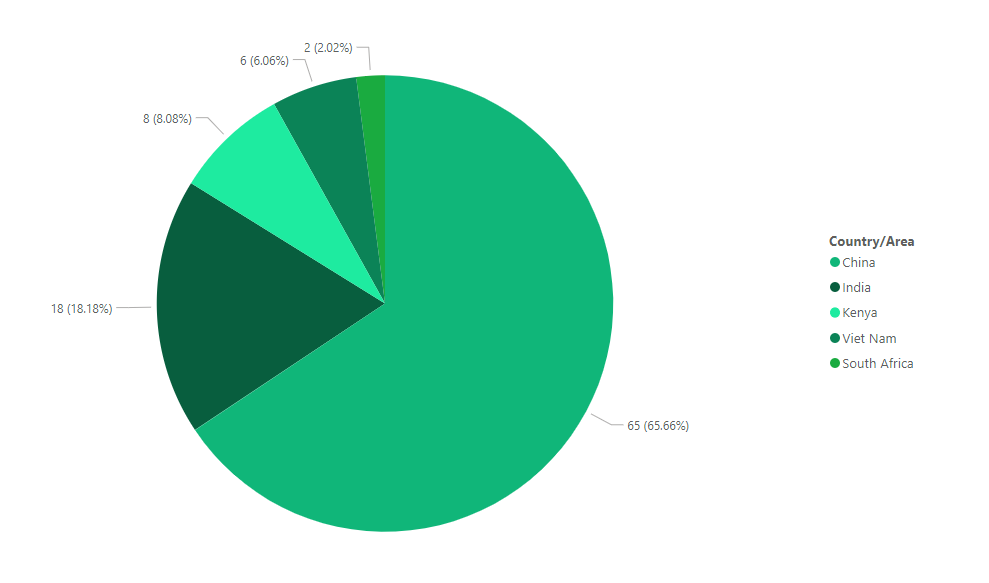
Figure 5: SD VISta projects in development w.r.t Countries (Source: Calculus IQ)
As seen in Figure 5, the future outlook for SD VISta projects varies across different countries, with China leading the way by hosting the highest number of in-development initiatives, accounting for 65% of the total projects. This can be attributed to China's commitment to sustainable development and its proactive efforts to address environmental challenges. The country's large population and rapidly growing economy necessitate significant investments in projects that deliver social and environmental benefits. Additionally, China's robust regulatory framework and government support for sustainable development initiatives create an enabling environment for SD VISta projects to thrive.
India ranks second in terms of in-development SD VISta projects, representing 18% of the total. India's strong focus on renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and poverty alleviation has fueled the growth of SD VISta initiatives in the country. The Indian government's policies and initiatives, such as the National Clean Development Mechanism Authority, have attracted project developers and investors to undertake projects that align with the SDGs.
Kenya, Vietnam, and South Africa follow suit with 8%, 6%, and 2% respectively. These countries have unique factors driving their SD VISta project development. Kenya's rich biodiversity and commitment to conservation contribute to the significant number of projects in the country.
Vietnam, with its growing economy and increasing environmental concerns, has recognized the importance of sustainable development and is actively pursuing SD VISta projects. South Africa's focus on renewable energy, water management, and social development has led to the emergence of several SD VISta initiatives.
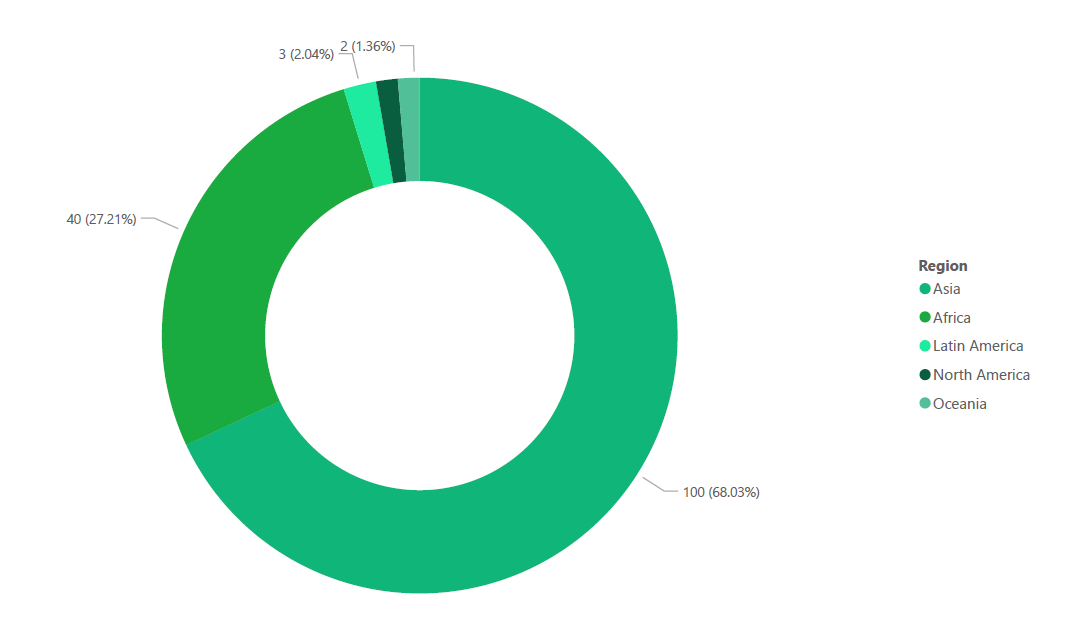
Figure 6: SD VISta projects in development w.r.t Region (Source: Calculus IQ)
As can be seen in Figure 6, the future outlook for SD VISta projects varies across different regions, with Asia taking the lead in terms of the number of in-development initiatives, accounting for 68% of the total projects. This can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, Asia is home to a large population and rapid economic growth, leading to increased demand for sustainable development initiatives. Additionally, the region faces significant environmental challenges, such as air pollution, deforestation, and water scarcity, which drive the need for SD VISta projects to address these issues. Moreover, governments in Asia have been actively promoting sustainable development and implementing policies that encourage investment in clean energy, green infrastructure, and social development.
Africa follows as the second region with a significant number of in-development SD VISta projects, representing 27.2% of the total. Africa's vast natural resources, diverse ecosystems, and rich biodiversity create opportunities for projects that focus on conservation, renewable energy, and poverty alleviation. Furthermore, the continent faces unique socio-economic challenges, such as access to clean water, healthcare, and education, making SD VISta initiatives crucial for sustainable development in the region. Efforts by African governments, international organizations, and private sector entities have fostered the growth of SD VISta projects across the continent.
Latin America, North America, and Oceania follow in terms of in-development SD VISta projects. The disparity between regions can be attributed to a combination of factors, including regional economic conditions, environmental priorities, policy frameworks, and the level of awareness and commitment to sustainable development. Each region has its own specific challenges and opportunities, shaping the demand and focus of SD VISta projects. It is important for regions to collaborate, share knowledge, and leverage their respective strengths to promote the adoption of SD VISta and achieve sustainable development goals on a global scale.
In summary, the distribution of in-development SD VISta projects across regions reflects the unique socio-economic and environmental contexts of each region. Asia leads the way due to its population size, economic growth, and environmental challenges, while Africa showcases its rich natural resources and socio-economic priorities. Collaborative efforts and knowledge sharing between regions can contribute to a more balanced distribution of SD VISta projects worldwide, fostering sustainable development across different parts of the globe.
If you are interested in learning more about the voluntary carbon market, we invite you to interact with Calculus IQ. This tool can help you explore different aspects of the market, including project types, retirement volumes, and more.
![[object Object]](/lib_ubcXiSgTRmkLVyyT/k8w528b9mk1p20to.png?w=400)
